Graphene - Electronic Properties and Defects
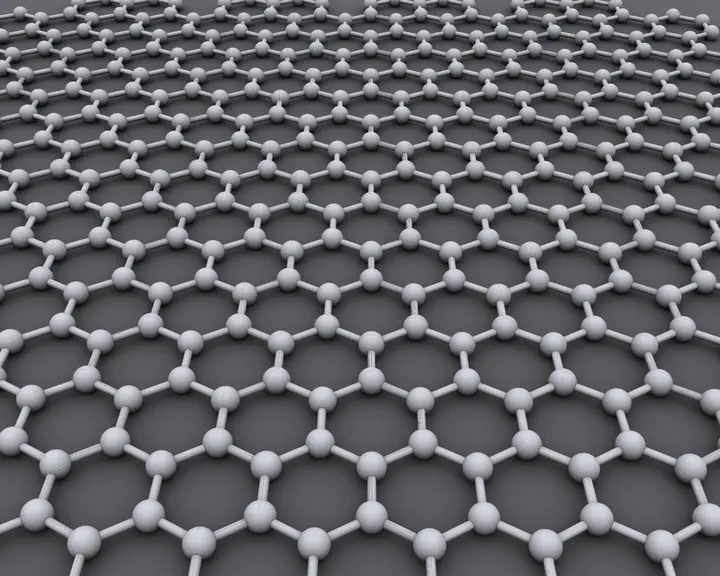 An illustration of the layers
An illustration of the layersAbstract
Graphene is one of the first 2-D materials to be discovered. We examine its physical structure and review the tight-binding model of Graphene with the next- nearest neighbour interaction. Only considering nearest neighbour hopping, we demonstrate the importance of Dirac points, the onset of the relativistic for- mulation and electrons acquiring pseudo-spin. We also show the e-h symmetry breaking on the inclusion of next-nearest hopping. Additionally, we derive the commonly stated density of states using Green’s function. Further, we model substitutional impurities in the Graphene lattice by the Slater-Koster model and derive the change in the band structure.